Understanding Linked Lists: Types, Use Cases, and How They Work
A beginner-friendly guide to linked lists — explore what they are, the different types, how they work, and where they're used in real-world programming.
🧠 What is a Linked List?

A linked list is like a chain of boxes.
Each box holds two things:
- Some data (like a number or name)
- A link (or pointer) to the next box
So instead of all data being packed tightly together (like in an array), it's scattered in memory — but linked together by these pointers.
📦 Real-Life Example
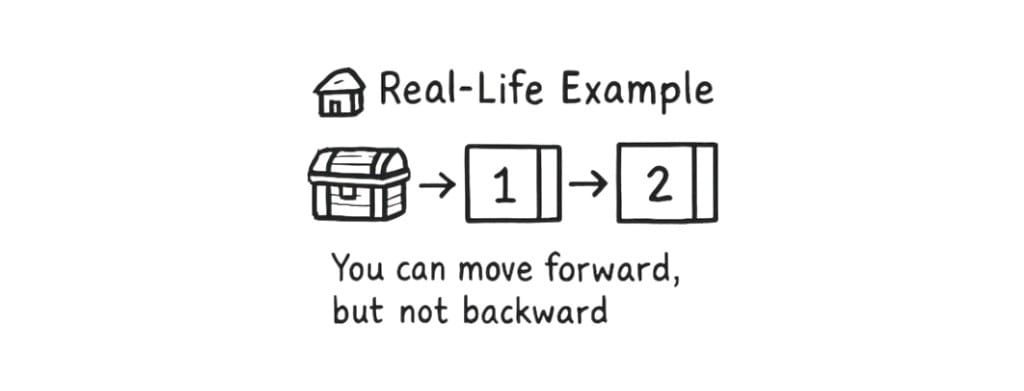
Imagine a treasure hunt.
Each clue (box) tells you what the next clue is.
You can’t jump to the 3rd clue directly — you have to follow one by one.
That’s how a linked list works!
🧱 Structure of a Node
Each part of the list is called a node.
It looks like this:
[ DATA | NEXT ]- DATA: the information
- NEXT: tells where the next box is
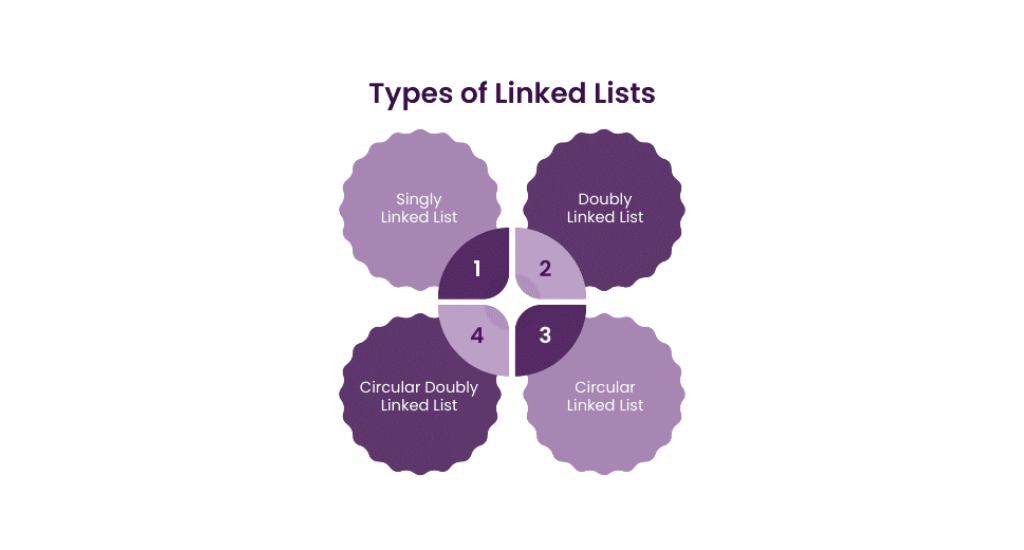
🔄 Types of Linked Lists
1. Singly Linked List
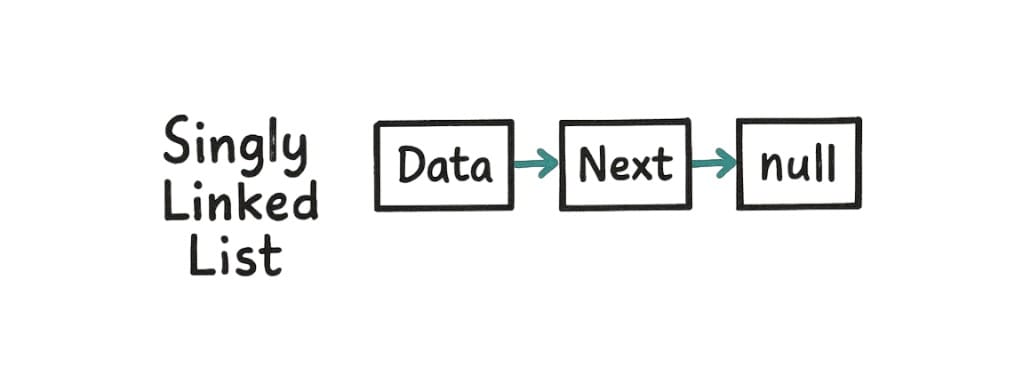
Each node points to the next node.
[1] → [2] → [3] → [null]You can move forward, but not backward.
2. Doubly Linked List
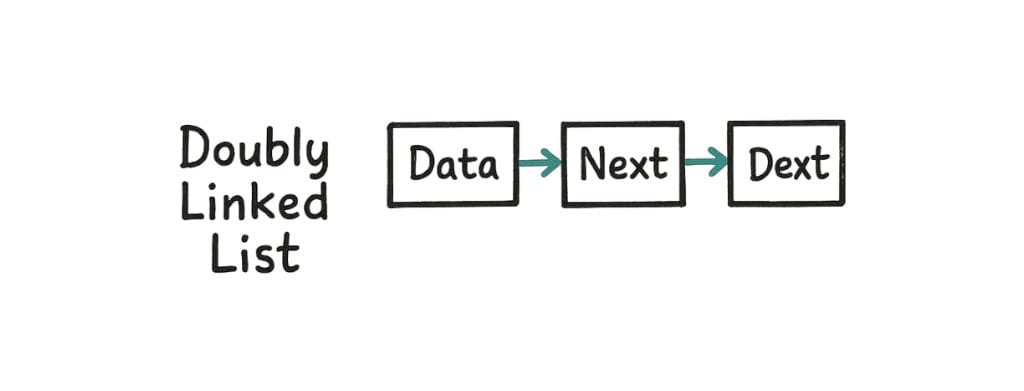
Each node points to both the next and the previous node.
null ← [1] ⇄ [2] ⇄ [3] → null
Now, you can move forward and backward.
3. Circular Linked List
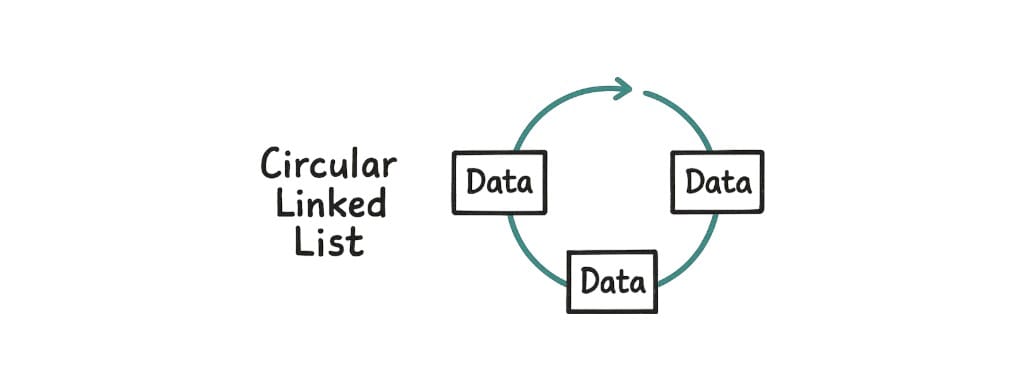
The last node connects back to the first one.
[1] → [2] → [3] → [1] → ...It becomes a loop. Great for things that keep repeating, like music playlists.
4. Circular Doubly Linked List
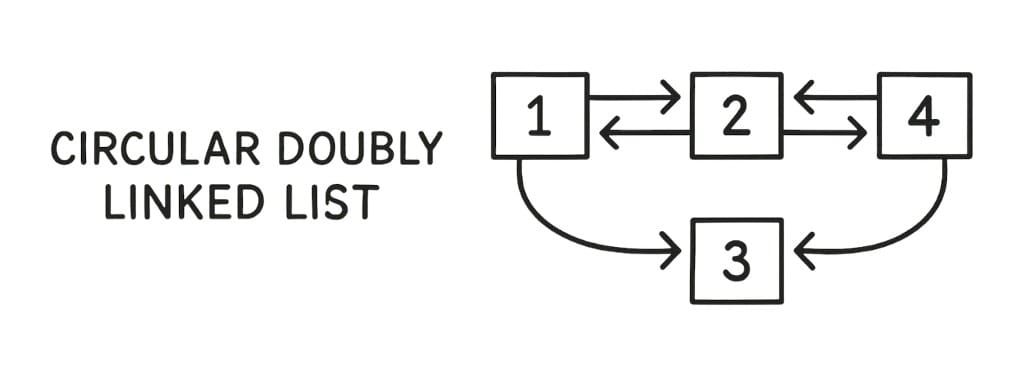
This one combines both ideas:
It’s doubly linked and circular — you can move forward and backward, and the ends connect.
[1] ⇄ [2] ⇄ [3]
↑ ↓
←–––––––––––––It never ends — useful for things like game loops, task schedulers, or tab switchers.
💡 Why Use Linked Lists?
- You don’t know the size of your data in advance.
- You often add or remove items in the middle.
- You need something lighter than arrays for certain memory tasks.
🧰 Where Do We Use Linked Lists?
- Undo/Redo buttons in apps
- Browser history (back/forward)
- Music players (next/previous song)
- Custom data structures like stacks, queues
📦 Summary
- A linked list is a chain of connected nodes.
- It’s different from arrays because it's flexible and dynamic.
- Now you know 4 types:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Circular Doubly Linked List
✍️ Final Thoughts
Linked lists are simple but powerful.
They help manage data dynamically and are used behind the scenes in many tools you use every day.
Learning them is a great step toward understanding how memory and structures work in programming.
